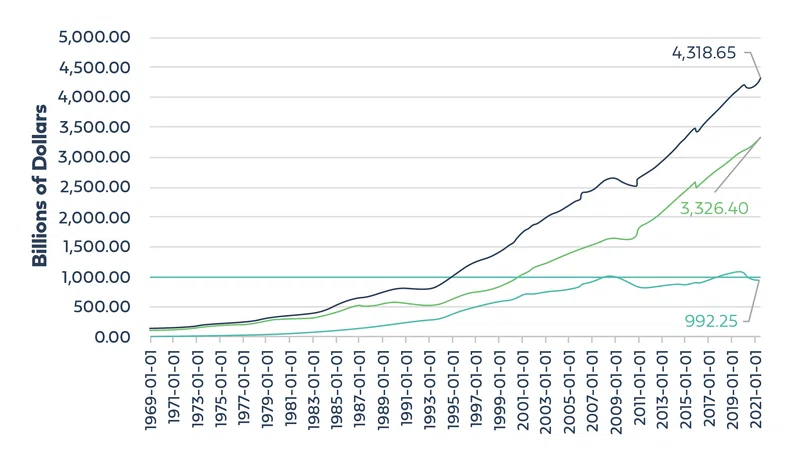
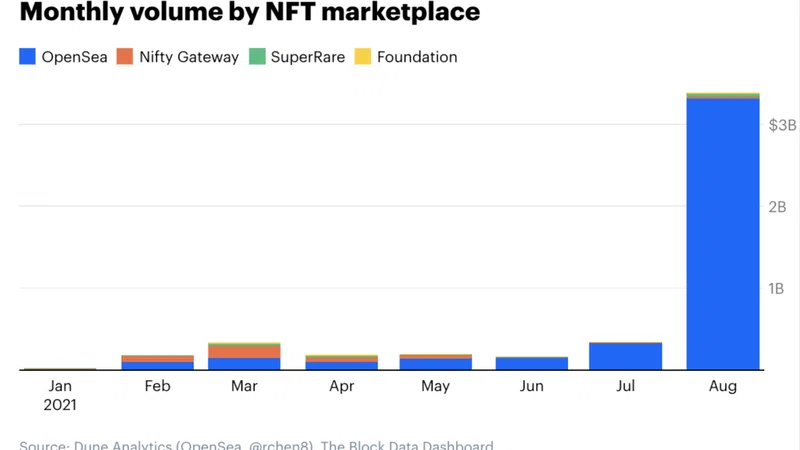
So you’ve been hearing more and more about this mysterious NFT topic, and you’re ready to find out what it’s all really about. You’re in the right place! We’re going to go over the basics of NFTs and demystify some common areas of confusion and misconception. Ready?
Let’s start with the name. NFT stands for non-fungible token. Don’t worry; it’s not as complicated as it sounds. ‘Fungible’ means that something can be traded, like physical currency or cryptocurrencies. So, a non-fungible token means that this particular token can’t be traded for another one. Why? Because NFTs are digital representations of assets, and those assets can be nearly anything. An NFT isn’t a currency; it’s basically a certification of authenticity for a digital asset. Frequently, these assets are collectibles, like sports memorabilia, but they’re digital.
You might be asking why anyone would bother paying for something like this, and it’s a good question. Digital art is one of the best examples to explain this. If we think about physical art and how much people value it (think of a painting from a renowned artist like Monet selling at a world-class auction house for tens or hundreds of millions of dollars), the actual value lies in having the original. Anyone can go online and look at a digital representation of a Monet painting, but only one person in the world will be the owner of that piece. Scarcity creates demand, and NFTs allow for scarcity to be created around digital items.
Next, let’s talk about how NFTs are created and why they’re secure. If you’re familiar at all with how cryptocurrency works, then you’re well on your way to understanding how NFTs are created. NFTs use the same blockchain algorithm that cryptocurrencies like Ethereum use. This allows the NFT creator to build in unique information to each NFT, making every one unique and distinguishable from all other NFTs. This also means that you can easily transfer ownership, and NFTs can be added together to create an entirely new NFT with its own identifiers.
Where Do NFTs Get Bought Or Sold?
Rarible – This peer-to-peer platform is great for perusing collectibles and getting your feet wet in the NFT world.
OpenSea.io – Similar to Rarible, OpenSea is an established peer-to-peer NFT platform that connects artists and sellers directly with buyers.
Foundation – Foundation is a different setup than Rarible and OpenSea in that there is a cost for artists to put their work on Foundation, and they must also be endorsed by a current artist to be approved. This promotes legitimacy and high-quality work but can also mean a higher price point for buyers.
All of the platforms mentioned here require you to purchase NFTs with cryptocurrency. Not all platforms accept all forms of crypto, so you’ll have to make sure you have a digital wallet and the approved form of crypto to purchase NFTs on these platforms. NFT Digital Art
Digital art is one of the most popular ways that NFTs are used. The process of creating a unique token for a piece of artwork allows the artist to verify the authenticity of the piece, thereby creating scarcity around it. On the buyer side, the NFT use of blockchain means that hacking the NFT and creating a fake is much less likely.
Of course, like physical art, there is the opportunity for hackers to “forge” artwork, but it becomes much less likely using blockchain.
NFTs In Real Estate
NFTs in real estate are broken into two categories, entire asset (EA) and fractional ownership (FO). Fractional ownership NFTs are more common because they essentially work as stock in a company. You could purchase an NFT representing a portion of a real estate company, and you would be paid out accordingly based on profits. In this case, an NFT is treated similarly to stock and is intended to be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Entire asset NFTs are much more complicated because we don’t have the class of ownership in place yet to tokenize an entire property.
Here’s a fun, very 21st-century concept—online real estate. Metaworld platforms like Roblox and Decentraland are virtual worlds that now offer real estate opportunities. Essentially, they work just like physical world real estate. There are a limited number of parcels available in varying locations, and they are bought and sold as NFTs. The future is here.
NFTs In Gaming
Gamers, get ready! Going on quests and winning battles with game characters that are in themselves NFTs can now earn you crypto, which you can exchange for traditional currency. Axie Infinity is a great example of one of these types of games, where characters are NFTs called Axies, and their trainers win more in battles or breed new ones from their existing Axies. These trainers can then sell their Axies to other players.
Another significant way the NFTs show up in gaming is in wearables, like sneakers. Digital artists create 3D sneaker designs that players can wear in games like Fortnite. The train doesn’t stop at shoes, though. Game skins, avatars, and all kinds of in-game options are being created and tokenized.
What About Music NFTs?
NFTs in music is a potentially game-changing swing in the industry for musicians. By tokenizing their work, artists can monetize their songs while at the same time bringing fans on board for the journey of that piece of work. An additional benefit is that an NFT can be created or “minted” with programming that automatically gives the musician a royalty each time the NFT is sold. Given the significant challenge that digital music has presented artists with over the past two decades, tokenizing their work could be a great way to help ensure our favorite musicians are getting paid for their work.
Can I Make Money On NFTs?
Simply put—you can. But, they can also suddenly become worthless with no notice. The value of an NFT is in what someone else is willing to pay for it. Once you’ve purchased one, you can’t simply trade it in for a cryptocurrency, exchange that for real-world money, and be on your way. You have to find someone who sees value in whatever your NFT represents and is willing to purchase it.
Of course, this can be likened to any number of real-world examples. Say you purchase a home, and then a massive overpass is put up right next to it. Your property value won’t be zero, but it will lose value because the perception will be that it’s now less desirable and therefore worth less than it was when you paid for it. Or, to make it even more simple—Beanie Babies, anyone?
The Future Of NFTs
NFTs have only been around for a few years and have only started becoming more mainstream in the recent past, so predicting their future use is murky at best. There are essentially two camps—those that think NFTs will be adopted as commonplace and will revolutionize the way we interact online, and those that believe NFTs will go the course of the Beanie Baby.
The notable difference between something that is purely a collectible, like the classic Beanie Baby example, and NFTs, is that NFTs can be used to verify the ownership and authenticity of an individually created product like art or music. NFTs have more of a function than a traditional collectible, so what happens remains to be seen!
Now that you have the nuts and bolts of what an NFT is, how they are made, and where to find them, you can decide whether this is an experiment that you’ll be trying for yourself or whether you’ll let some more time go by before dipping your toe into the NFT waters.